ONDC - the new kid on the e-commerce block!
Let us begin with asking you a question, of which, we know you know the answer, and you know that as well. But let’s do it anyway.
So, here it goes – When someone says the words ‘e-commerce in India’ what are the first words or names that come to your mind? And obviously, as expected, the first two names would be – Amazon and FlipKart. Then possibly Meesho, Udaan and a few more. Snapdeal and PayTm dropped out of this list long back.
This is about to change with ONDC. Now this brings us to the question –
What is ONDC?

ONDC is an initiative of the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry – ONDC stands for Open Network for Digital Commerce and intends to do exactly what the name says.
Established as a private non-profit company, ONDC aims at creating a digital infrastructure that will enable sellers to voluntarily display their products and services across all participating apps and platforms. The open network will thus help buyers on the other hand to access one product from more than one platform without actually being on the platform itself.
The scope of ONDC however will not be limited to product based e-commerce but will include segments like hotel booking, travel, food order and delivery, to be discovered and engaged by any network-enabled application.
As per an article released by Press Information Bureau, Government of India, Ministry of Commerce & Industry on 6th April 2022 –
“Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is an initiative aiming at promoting open networks for all aspects of exchange of goods and services over digital or electronic networks. ONDC is to be based on open-sourced methodology, using open specifications and open network protocols independent of any specific platform.”
https://pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRID=1814143
Who all are a part of the ONDC?
Various public and private sector banks have already acquired stakes in ONDC. 24 companies, such as Flipkart-backed Ekart Logistics, hyperlocal quick commerce firm Dunzo, and digital payments firm PhonePe, are reported to be in the process of integrating with ONDC. Google is also in discussion with ONDC on how to integrate its services with the network.
Microsoft, Kotak, PhonePe, and Snapdeal are among the companies in the “advanced stage of development”, while Airtel, Axis Bank, HDFC Bank, India Post and hundreds of other businesses have “initiated integration” with the network, according to the ONDC website.

Is ONDC live for business?

On April 29th 2022, ONDC was rolled out as a pilot project in 5 Indian cities across different geographical regions in India – Delhi NCR (National Capital Region), Bhopal, Bengaluru, Shillong, and Coimbatore.
At present, the focus of operations is on retail and restaurants and facilitating real-time transactions, the open network will soon extend to other categories like travel and mobility. The goal is to accommodate 30 million sellers and 10 million merchants online.
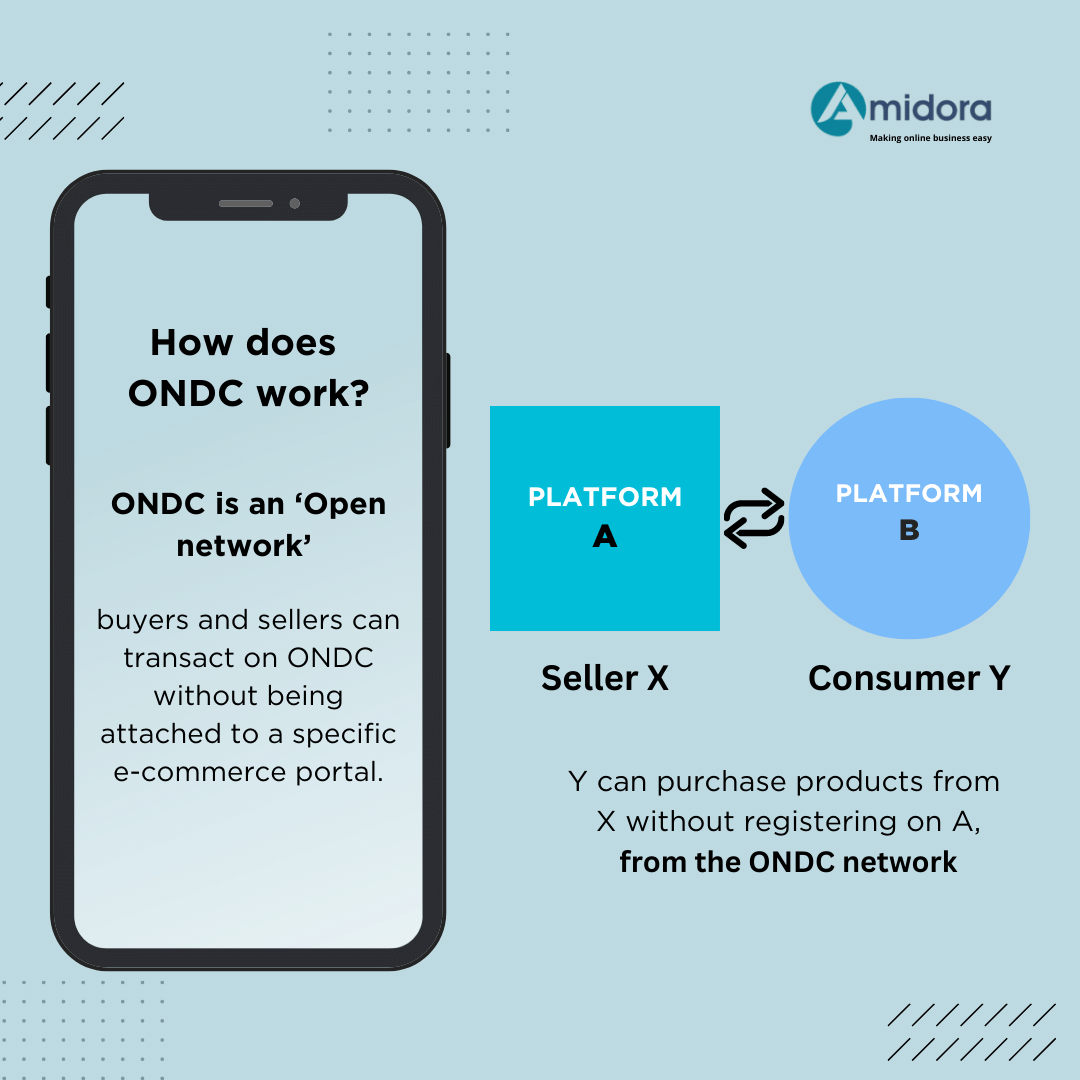
How does ONDC work?
ONDC being an open network means that buyers and sellers can transact on ONDC irrespective of whether they are attached to any specific e-commerce portal.
For example, even if a seller X is registered on platform A, while the consumer is registered on platform B, the consumer can directly purchase products of seller X without registering on platform A from the ONDC network.
The ONDC platform lies in the middle of the interfaces hosting the buyers and the sellers. Currently, the buyer side interface is being hosted by Paytm, whereas the seller side interface is being hosted by other players like GoFrugal, etc.
When a buyer searches for an item on the Paytm app, the app will connect to the ONDC platform from where ONDC has gone live, which will connect it to seller side interfaces that will list all the companies from where you can buy the particular item.
Similarly, with ONDC implemented, a user searching for a Bluetooth headset on Amazon would also see results from Flipkart on the Amazon app.
Parties involved in ONDC?
Any digital transactions platform will need more parties than just buyers and sellers. Any entity that wants to be part of ONDC has to play one or more of the following roles:

Connecting buyers to the network:
creating applications or websites that customers will access to browse and search for products that are on sale on the ONDC network. At the moment, only Paytm has built a buyer-side interface.
Connecting buyers to the network:
creating applications or websites that customers will access to browse and search for products that are on sale on the ONDC network. At the moment, only Paytm has built a buyer-side interface.
Gateway:
Applications that will broadcast the search request received from buyer-side apps to seller-side apps listed on the ONDC registry, based on search criteria.
ONDC's role in democratizing India’s growing e-commerce market -
ONDC being built on an open source platform, implies that the technology or code deployed for the process is freely made available for everyone to use, redistribute, and modify. It thus aims at fostering open networks developed on open-sourced methodology, using open specifications and network protocols, and independent of any specific platform.
In a multilingual country like India, its focus would be on small merchants and rural consumers, with apps in Indian languages.
It will give an opportunity to users to rate the service providers and it will be visible across the network. It will also stop the preferential treatment given to selected sellers.
Since ONDC will not be following a platform-centric model, it will help the country’s smaller businesses to come online and offer their products for sale. This means that millions of small retailers and kirana stores will now get an equal opportunity to showcase their products online,
Since ONDC is not platform-centric, it will also help match the online consumer’s demand with the nearest available source of supply. By this way consumers can find any seller, product, or service via any compatible application or platform – offering real freedom of choice.



It will therefore restrict concentrating power with a handful of players. And this approach will allow consumers and sellers to choose which apps they want to use to access a single network. Another way ONDC will help the sellers currently selling on Marketplaces is by helping them move out of the platform ecosystem along with the value they have created which otherwise is locked within the platforms they operate in.
Once ONDC is implemented throughout the country, it would provide a big boost to all the small retailers and businesses which so far could not be a part of India’s growing e-commerce story. These small businesses are expected to benefit from transparent rules, lightweight investment, and lower cost of business acquisition.
With deep pockets, US based Amazon and Walmart owned Flipkart have spent a cumulative US$24 billion to capture 80 percent of the Indian e-commerce market, including their market budgets and aggressive discounts. Indian retail giants like Reliance and Tata have also launched their proprietary retail platforms and shopping apps
To summarize -

ONDC - one page summary
ONDC is still a very new concept. It is very easy for people to get confused about what it will do and what it will not. To make everyone’s life easier, we have put the summarized all that in just one infographic.
This will help anyone understand –
What ONDC is and what it is not.
What it will do and it will stay away from.
ONDC's Targets in numbers -
With a target to bring some form of equality between the various seller segments and groups, ONDC has its eyes set on some big targets.
In the next 5 years, ONDC aims to -
Increase e-commerce penetration to 25%
sign up 900 million buyers
1.2 million sellers
achieve GMV (gross merchandise value) of $48 billion.
The Indian government estimates that India’s e-commerce market was worth more than $55 billion in gross merchandise value in 2021 and will grow to $350 billion by the end of this decade.

What are the challenges ONDC might have to face?

No one would seem to disagree that implementing ONDC is a herculean task, one that will have its own set of challenges.
For almost a decade now, Amidora Infotech has been enabling offline businesses to go online and grow as well. We have seen the nitty gritties of this business and we believe the road to complete implementation of ONDC will not be easy.
Here is what we feel are the challenges ONDC will face in the times to come.
